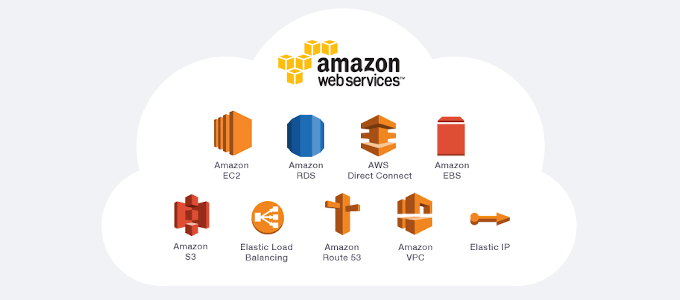
Cloud computing is the use of remote servers on the internet to store, manage and process data rather than a local server or personal computer. Cloud computing comes in three basic categories beginning with Software as a Service (SaaS) which reduces company expenditure by providing a cloud server with software already included. Platform as a Service (PaaS) lets developers build apps and collaborate on various projects without the need to purchase or maintain infrastructure. Last, we have Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) which is what AWS falls under more so than the others. IaaS provides companies the chance to rent servers, storage, security, etc. from a cloud provider.
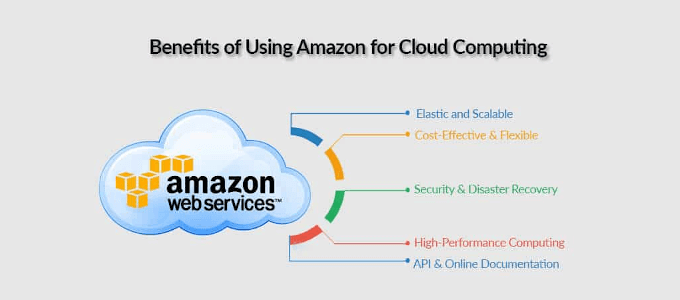
The Benefits of AWS
Cost
Companies used to have to physically build a storage space in order to store large amounts of data and maintain it themselves. Choosing to store data on the cloud came at considerable expense on top of lengthy contracts that had the potential to hinder company growth. Purchasing more space than needed could become too expensive, while purchasing too little could prove disastrous. The same principle applied to computing power. Sustaining business at peak times required that companies buy more power. The problem was during off-peak times when the power was no longer required. The company would still have to pay for power they weren’t even using. AWS allows companies to only pay for what they use. With no upfront costs on storage and infrastructure, there is no longer a need to estimate usage versus cost. AWS scales cost automatically to the needs of its customers.
Scalability
AWS continues to provide resources in aid of expansion as a business continues to grow thanks to a flexible usage business model. Customers no longer need to revisit a discussion about whether their current budget for computer usage is necessary. In some circumstances when pertaining to AWS’s scalability, a company can use AWS to “set it and forget it.”
Security and Reliability
AWS has servers located within 76 availability zones, spanning 245 countries and territories. These zones have been divided not only to give users a choice in setting geographical limits on their services, but also to diversify physical locations, providing stronger security and avoiding permanent data loss worldwide. The training and certification of AWS has also become a much sought after and high in-demand validation by professionals and organizations in need of innovative teams for cloud initiatives. AWS is not without its disadvantages, primarily dealing with EC2’s region to region default resource limits and other general cloud computing issues like server downtime and limited control.